
Templates Community /
PID Temperature Controller
PID Temperature Controller
Captain O Captain
Published on 2020-10-12

1. Introduction
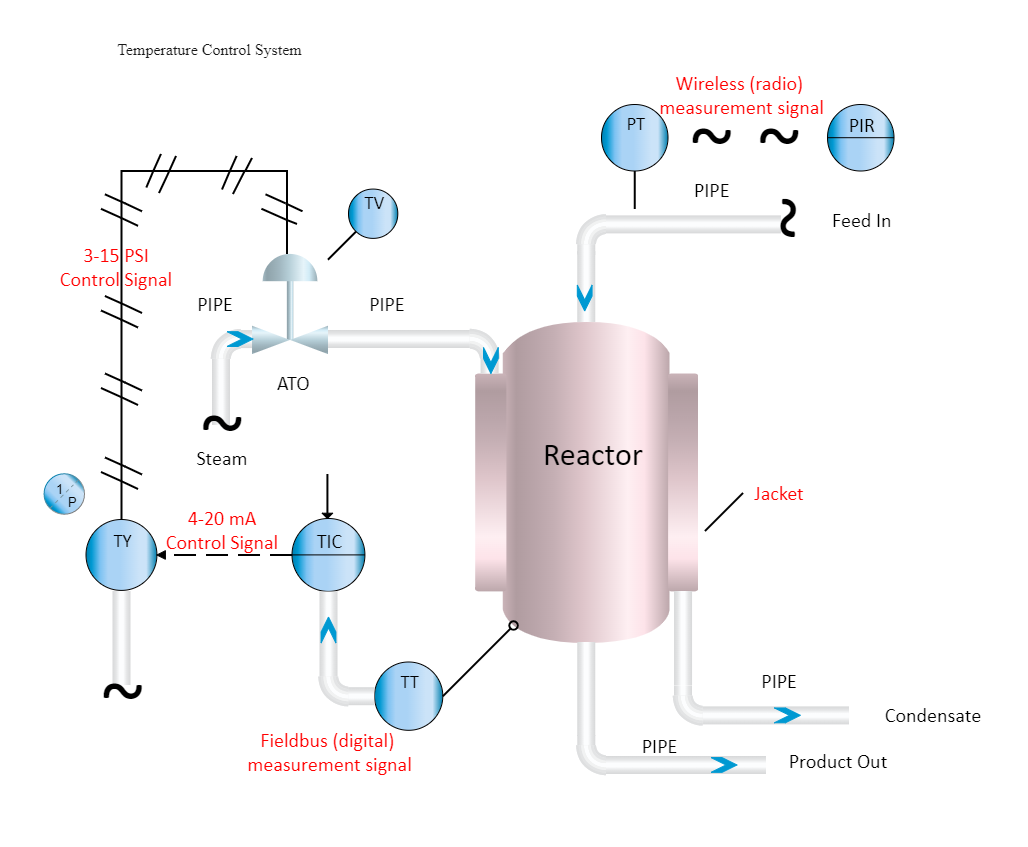
A temperature controller, also known as a PID controller, is an instrument that is used to control temperature. The temperature controller receives data from a temperature sensor and outputs it to a control device, such as a heater or fan.
A temperature control system relies on a controller, which receives a temperature sensor such as a thermocouple or RTD as input to reliably control process temperature without considerable operator participation. It does a comparison between the current temperature and the intended control temperature, or setpoint, and sends a signal to a control element.
2. The Usage of PID Template Controller
Most process controllers have PID temperature control as a loop control feature to improve process accuracy. PID temperature controllers use a formula to calculate the difference between the desired temperature setpoint and the current process temperature, and then predict how much power to use in subsequent process cycles to keep the process temperature as close to the setpoint as possible while minimizing the impact of process environment changes.
PID temperature controllers are distinct from On/Off temperature controls, which operate at full power until the setpoint is reached. Temperature controllers with PID are more successful at dealing with process disruptions, which can be as simple as opening an oven door, but the change in temperature can have an impact on the final product's quality. If the PID temperature controller is properly tuned, it will compensate for the disturbance and return the process temperature to the setpoint.
3. How to Create a PID Temperature Controller
Step 1: Define the system's scope.
Do you need to understand the overall process before drawing a P&ID? What does it accomplish?
Step 2: Make a list of the inputs.
Is it a manual or an automatic system? Where do the inputs come from and where do they lead?
Step 3: Determine the outcomes
What is the final result? What are you going to need to make it happen?
Step 4: Make a list of all the equipment involved in the process.
Consider the instruments, control devices, pipelines, and other machinery.
Step 5: Define the components' relationships.
What is their relationship like? Are they a good match?
Step 6: Put your flow together.
Start at the beginning or conclusion of the procedure and work your way through it step by step. What is the next step in the system?
Step 7: Fill in the details
Details on the pipe, component, and instruments, such as measures and diameters, should be added.
Step 8: Go over the steps again.
Keep an eye out for inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
Tag
PID
PID Collection
pid environmental
Share
Report
18
1.9k

Post
Recommended Templates
Loading
