
Templates Community /
Logical Network Diagram
Logical Network Diagram
Joy
Published on 2020-10-23

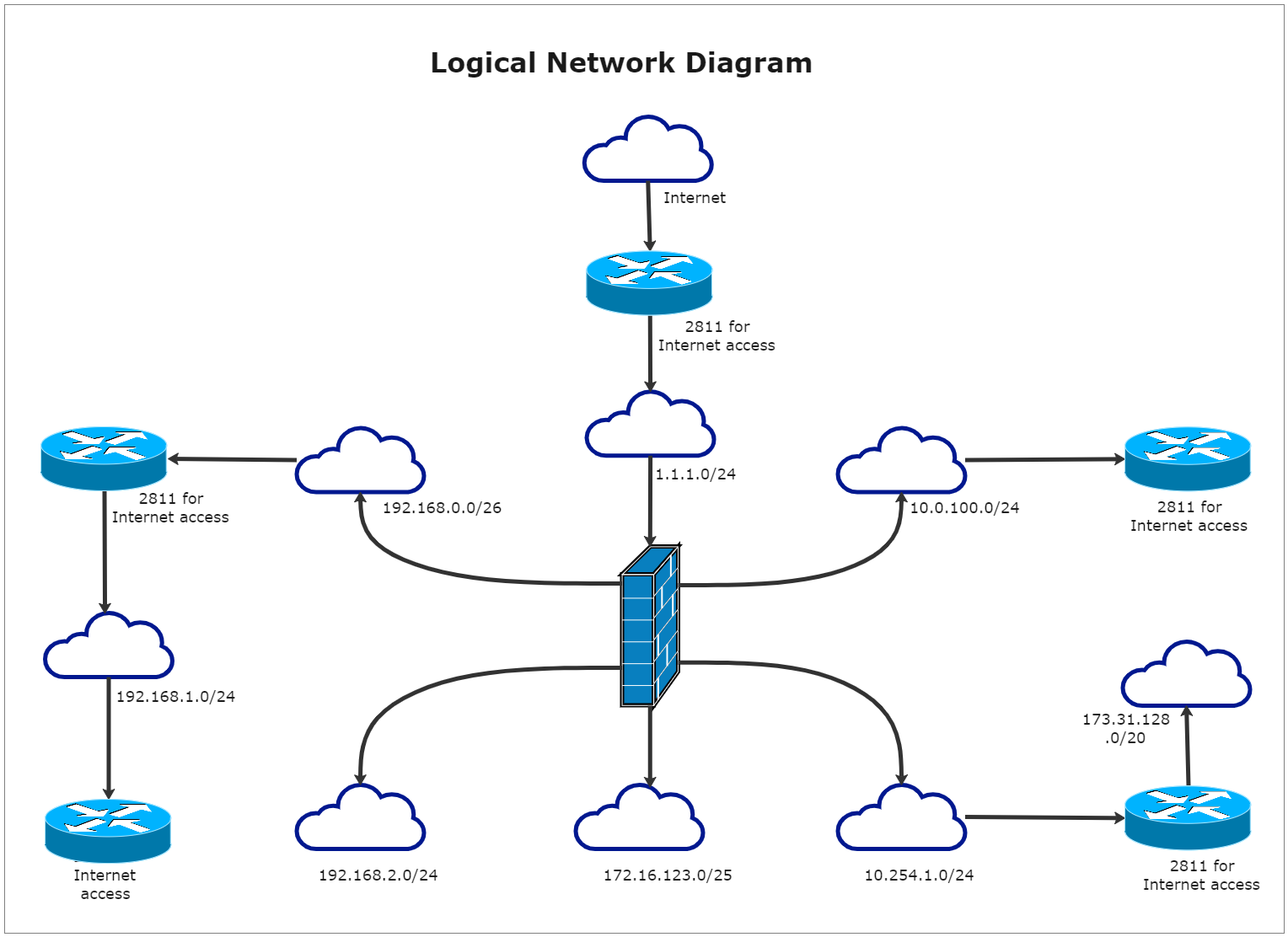
The Logical Network Diagram depicts how information flow occurs in a network, allowing users to see subnets, network devices, and routing protocols. It helps in visualizing networks' logical structure. Unlike a physical network, a logical network frequently spans several physical objects such as network nodes and networking equipment that are frequently part of other physical networks. It can also cover simply a tiny portion of a single device. A logical network, for example, can be made up of elements from separate networks with devices located all over the world, as in a global enterprise where the computers of site managers from different countries may be connected as a single logical network to foster quick and hassle-free communication despite the fact that they are separated by continents. A logical network might also be built of numerous virtual machines and virtual networking entities, all of which live on a single physical server at the most basic virtual level.
Tag
Logical Network Diagram
Network Diagram Collection
Share
Report
19
2.5k

Post
Recommended Templates
Loading
