
Templates Community /
Amine Absorption
Amine Absorption
Joy
Published on 2020-12-01

Amine absorption is commonly used for gas sweetening in the oil and gas industry and is
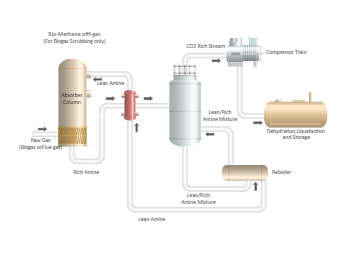
therefore more readily available. It is also technically feasible in terms of maintenance capabilities and custom design. It utilises an amine solution (usually Monoethanolamine (MEA)) in counter flow with raw biogas to absorb CO2 and H2S, in an absorber column operating close to ambient conditions.
The rich amine solution is then boiled in a reboiler, allowing the CO2 and H2S to be released as gaseous vapour in the stripper column (Figure 1). The lean amine solution is then recirculated to the absorber column whilst the CO2 gas stream is further treated to meet food grade specifications
Tag
P&ID
Share
Report
8
844

Post
Recommended Templates
Loading
