
Templates Community /
Eukaryotic Phylogenetic Tree
Eukaryotic Phylogenetic Tree
Pathy
Published on 2021-10-19

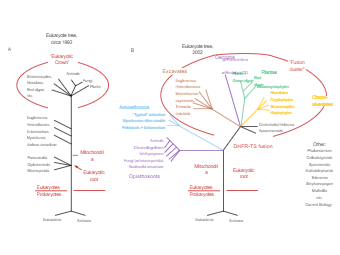
Eukaryotic Phylogenetic Tree shows how the eukaryote Tree of Life (eToL) represents the phylogeny of all eukaryotic lineages, with the vast bulk of this diversity comprising microbial 'protists.' Most of the described species of eukaryotes belong to the multicellular groups of animals (Metazoa), land plants, and fungi; it has long been clear that these three 'kingdoms' represent only a small proportion of high-level eukaryote diversity. It should be noted here that Phylogenetic trees are so useful because they provide the historical narrative for explaining the similarities and differences among those entities placed on the tree. A phylogenetic tree is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics.
Tag
Phylogenetic Tree
Share
Report
1
234

Post
Recommended Templates
Loading
