
Templates Community /
Bacteria Phylogenetic Tree
Bacteria Phylogenetic Tree
Pathy
Published on 2021-10-19

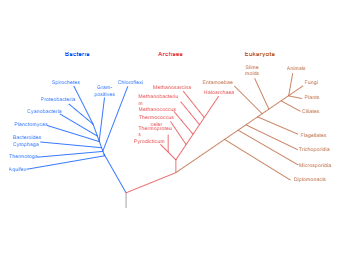
The below bacteria, archaea, and eukarya are represented by a phylogenetic tree. This will help you study the biology of bacteria and other fungi, plants, ciliates, flagellates, diplomonads, and more. Many phylogenetic trees have a single lineage at the base representing a common ancestor. Scientists call such trees' rooted,' which means there is a single ancestral lineage (typically drawn from the bottom or left) to which all organisms represented in the diagram relate. As the phylogenetic tree diagram suggests, the major components of such trees are leaves. The leaves of a tree can be species, populations, individuals, or even genes. If the tips represent a formally named group, they are called taxa (singular: taxon). A 'taxon' is a group of organisms at any hierarchical rank, such as a family, genus, or species.
Tag
Phylogenetic Tree
Share
Report
4
609

Post
Recommended Templates
Loading
