
Templates Community /
Learning Theories
Learning Theories
Rachel Lockman
Published on 2021-12-16

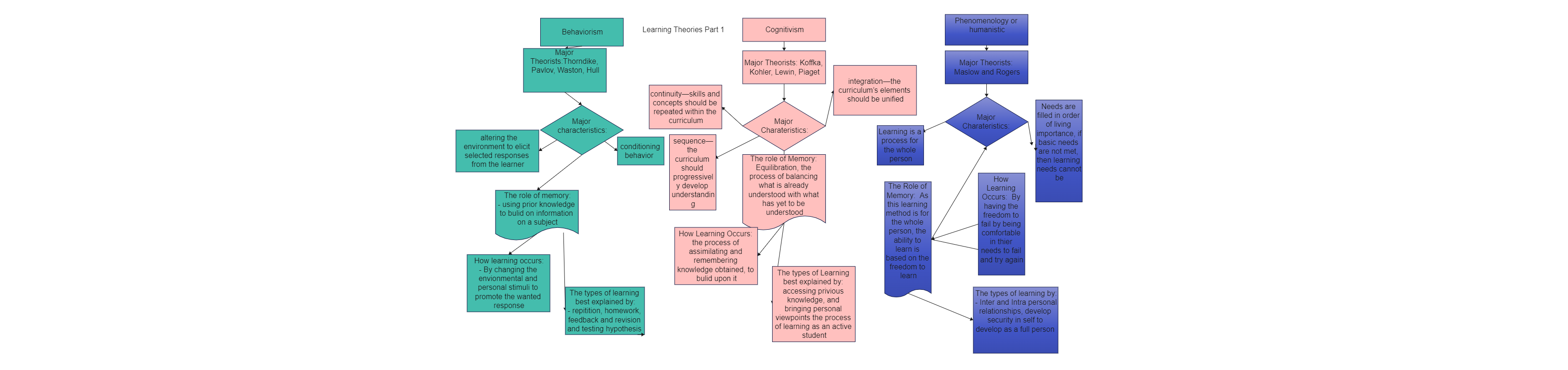
As the learning theories diagram suggests, there are five primary educational learning theories: behaviorism, cognitive, constructivism, humanism, and connections. It should be noted here that learning is defined as a process that brings together personal and environmental experiences and influences for acquiring, enriching, or modifying one's knowledge, skills, values, attitudes, behavior, and worldviews. Behaviorism is only concerned with observable stimulus-response behaviors, as they can be studied in a systematic and observable manner. As the map illustrates, cognitivism relies on external factors (like information or data) and the internal thought process. Constructivism is where the learner builds upon his or her previous experience and understanding to "construct" a new understanding. Humanism is a "learner-centric approach" whose potential is the focus rather than the method or materials. Connectivism is what is informed by the digital age. It departs from constructivism by identifying and remediating gaps in knowledge.
Tag
diagram
education
Share
Report
0
103

Post
Recommended Templates
Loading
