
Templates Community /
Meta Analysis
Meta Analysis
Community Helper
Published on 2022-08-24

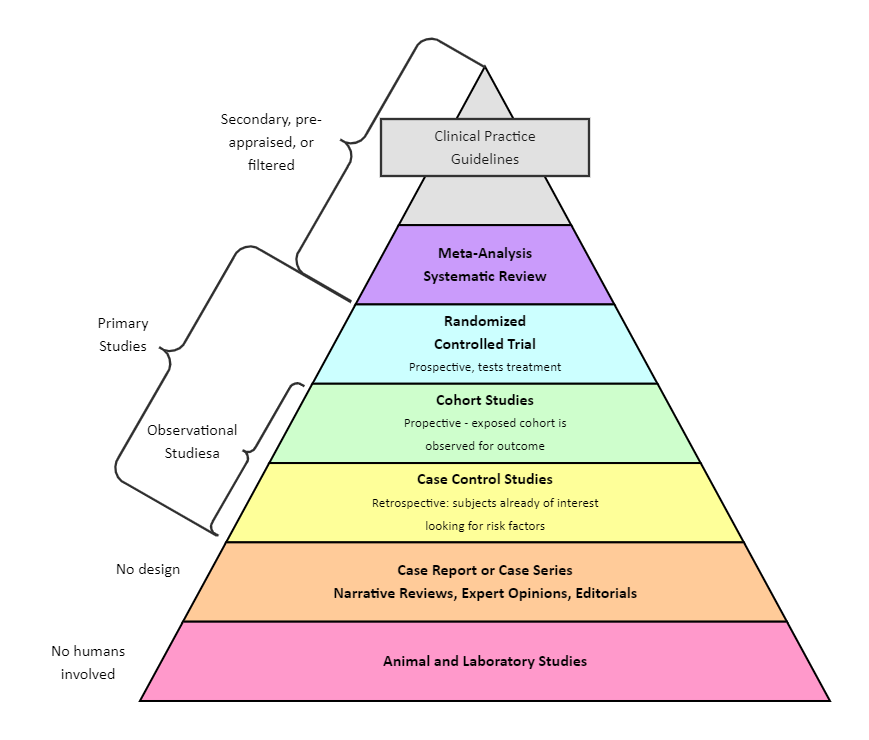
Meta-analysis is a research process that uses statistical methods to calculate an overall or 'absolute' effect by systematically synthesizing or merging the findings of single, independent studies. Meta-analysis does not simply combine data from smaller studies to increase the sample size. Analysts employ well-established, systematic methods to account for differences in sample size, variability (heterogeneity) in study approach and findings (treatment effects), and to assess the sensitivity of their results to their systematic review protocol (study selection and statistical analysis). Following the selection of studies for inclusion in the meta-analysis, summary data or outcomes are extracted from each study. Furthermore, sample sizes and data variability measures for both the intervention and control groups are required.
Tag
Agile business analyst
Business Analysis
business analysis diagram
Share
Report
1
230

Post
Recommended Templates
Loading
