Ecommerce Value Chain Analysis

1. Introduction
Years after the complete development of the Internet and its main features, the world is still measuring the long-term consequences and effects of this revolution. Beyond any doubt, it has changed many aspects of technology usage and development, as almost everything in modern life needs to be linked to the World Wide Web to be effective and successful. No matter if it is a single organizational page, a business, a big corporation, or a personal project, if it is not properly designed to function on this virtual field, it’s probably condemned to fail. One noticeable effect of the Internet revolution is E-commerce development. Ecommerce is no other thing than buying and selling goods and services within the Internet, and through all the devices that can connect people and organizations to it. In this article, we are going to specifically address the E-commerce Value Chain.
2. Background of Ecommerce Industry
The E-commerce industry did not immediately start with the Internet. It still required a few years to emerge, given the slow development of some Internet features, and more specifically, the implementation of some virtual payment methods. After this, several business niches started to rapidly unveil, and some technology entrepreneurs were as fast to start to exploit them. Three kinds of Ecommerce were initially developed and exploited: B2B (Business to Business), B2C (Business to Consumer), and C2C (Consumer to Consumer). However, today, it’s said to be more than eleven Ecommerce business models detected by experts, and given the fast development of new devices and features, there could be many more in the shadows, ready to emerge.
With professor Porter's Value Chain tool of analysis, we can determine where are the E-commerce business model competitive advantages, and to do so, it is important to conduct a proper E-commerce Value Chain Analysis.
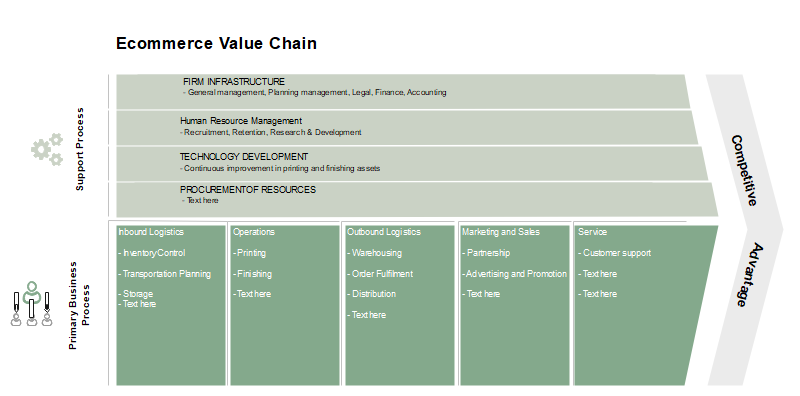
3. Primary Activities in Ecommerce Value Chain Analysis
As the first and important element in this kind of analysis is to determine the primary activities that add value while transforming raw material into finished goods, we are going to address each one of them.
Source: EdrawMax OnlineInbound Logistics:
Unless these processes are fully automated, is one of the aspects that usually need to be “manually” worked. Goods, inputs, and raw material need to be stored, inventoried, packaged, and moved through shops, distribution centers, fabrics, or manufacturing facilities. Even though, technology can still have a wide range of development here. Software and apps can easily be adapted to give smart solutions, as we can verify in some of the most successful E-commerce business models. Inventory control, transportation planning, storage, and tracking can benefit from technology solutions to reduce costs and achieve a competitive advantage.
Operations:
This is another field that can be fully improved by the use of technology. From the control and support of the supply chain to the improvement of the activities needed to fully cover the mission of an organization, technology automation, communication, and interconnection possibilities are huge in operations. One example of this can be found in Tesla Value Chain, as this is one of the aspects where they achieve competitive advantage by the “high integration of robots into various manufacturing processes”.
Outbound Logistics:
The E-commerce business model outbound logistics is experimenting a fast IT and technology development. Big corporations as Amazon, are starting to fully automate activities within their outbound logistics, including distribution and even delivery of products. But there's still plenty of fields to push this development even further. Order fulfillment, distribution, product tracking, and, in fact, delivery, can be subject of improvement by several kinds of technologies such as satellite positioning (GPS), robotics (through drones), communications (smartphone apps), security (cameras, alarms), and coding (programming), to radically reduce costs and achieve competitive advantage.
Marketing and Sales:
These activities have especially benefited from technology development. From software improvements to the targeting and segmentation of customers through social media platforms, the E-commerce business model depends highly on marketing and sales. However, and paradoxically, most E-commerce business models tend to decidedly reduce costs through smart strategies like “word of mouth” or Tesla’s “Zero Dollar Marketing”.
Service:
Maybe one of the E-commerce model aspects that is less addressed through technology, but it could be because most E-business goods and products don’t need gross service activities. Goods and products need to be in good shape and functional when customers receive them or will simply be returned. However, customer service can still be highly improved through automation and technology, and because of that, we are seeing a very fast growth of “virtual customer assistance” in several businesses. Beyond any doubt, this allows companies to reduce labor costs and achieve a competitive advantage or balance other expenses.
4. Support Activities in Ecommerce Value Chain Analysis
As the second step to properly conduct a Value Chain Analysis is to address the support activities, we are going to take a look into the E-commerce business model to determine where the use of technology can reduce cost and provide a competitive advantage.
Infrastructure:
Maybe is the moment to ask ourselves if a firm infrastructure can be determined or influenced by technology and the answer is, yes. The E-commerce business model is different from “Brick and Mortar” businesses, even though many firms will still maintain their old model if it is successful. Technology and IT can dramatically improve aspects like general management planning, project management, contract management, or accounting. Not in vain, there are several software solutions to help businesses with each one of these tasks. Therefore, and even when management can’t be automated, assistance tools can help to add value, reduce costs and achieve a competitive advantage.
Human Resource Management:
This is one of the E-commerce business model aspects that could be less influenced by technology. Ecommerce firm’s stills need to develop solid strategies to catch, retain, promote and manage their human resources. However, as it happens with general management and planning, assistance tools can still be determinant to cut expenses and add value, reducing assessment and decision times, and allowing to use only the necessary human workforce required to carry on certain activities. We can verify this in the form of several software solutions.
Technology Development:
Beyond any doubt, this is the field where technology is making the biggest steps and having determinant influence because the E-commerce business model needs to have unique and specifically tailored solutions to help and improve all the other activities in its value chain. As an immediate consequence of this, we can see how the firms have their own IT, technology, or technology development departments, almost always nearly connected and responding to general management. Big firms make the biggest investments in this area and it will keep growing in importance in the near future.
Procurement:
As a basic aspect of almost any business, the E-commerce model still needs to be sure to procure their raw material and inputs to transform into finished goods. Technology can be of great assistance in many ways here, from controlling and improving the supply chain, help to find the best suppliers in the market, the inputs with a cheaper price, or locating low-cost markets and make partnerships.
5. Key Takeaways
As aforementioned, the E-commerce model is a new and revolutionary way of making business in today’s competitive environment. It is different from old “Brick and Mortar” models and firm infrastructures are deeply determined not only by the model but by the scope. It allows to easily plan, adjust, and focus on almost every aspect of the value chain to reduce costs, add value, and achieve a competitive advantage over other businesses, even if they are in the same industry or niche.
We hope this Ecommerce Value Chain Analysis was helpful to unveil how the model can be subject to changes and improvements through technology and where in the chain can be aspects where strategies and tools can be determinant.
However, if you want to go deeper in conducting a Value Chain Analysis of these business models don’t forget to try EdrawMax Online. EdrawMax is a great tool to make business model diagrams to improve assessments and obtain better and accurate results. It has more than 280 templates that will, beyond any doubt, help you make an outstanding Ecommerce Value Chain Analysis. Also, you can find substantial value chain templates in our template community to have a quick start.
6. References
-
Dudovskiy, J. (2021) 'Tesla Value Chain Analysis', Business Research Methodology, [online]. Available at: https://research-methodology.net/tesla-value-chain-analysis-2/ (Accessed 13 August, 2021).
-
Murray, J. (2021) “Complete Ecommerce Supply Chain Guide”, [online] Available at: https://www.shipium.com/blog/ecommerce-supply-chain (Accessed 19th August, 2021).
-
Porter, M. (1998) “Competitive Advantage”. Free Press Editorial.
-
Zeng, Q. and Huang, L. (2004) “Identifying e-Business Models: A Value Chain Based Analysis”. Journal of Electronic Science and Technology of China, [online]. Available at: http://www.journal.uestc.edu.cn/fileDZKJDX_EN/journal/article/dzkjdxxbywb/2004/3/PDF/2004-3-146.pdf (Accessed 20th August, 2021).