IKEA PESTEL Analysis

1. Introduction
The PESTEL analysis of a business organization is pretty significant to understand its prospects. The PESTEL analysis is akin to a scientific investigation that takes the past and present position of a company into account to simulate its future progress. PESTEL analysis looks into the growth factors of a company. It also identifies the weaknesses or threats the company may face. IKEA is a well-known manufacturing company that widely deals with furniture and home accessories. PESTEL analysis of IKEA details the external economic, political, and social factors affecting its future expansion.
2. Background of IKEA
Basic information about IKEA is necessary to conduct a Pestle analysis of IKEA. The information regarding the establishment helps in clearly pointing out the strengths of the company and the challenges it had to face and might face in the future.
IKEA Group was initially under the parent organization of Stichting INGKA Foundation. Today it is famous as the largest manufacturer and retailer of furniture and appliances. Ingvar Kamprad in Småland on July 28, 1943 established the firm. The growth of this Swedish furniture multinational company is discernible from its expansive business empire that covers about 50 countries. The essential information about IKEA is discussed in detail in this PESTEL analysis.
2.1 Basic Information of IKEA
|
Company Name |
Inter IKEA Systems B.V. |
|
CEO |
Jesper Brodin, Jon Abrahamsson Ring |
|
Company Type |
Private |
|
Year Founded |
1943 |
|
Number of Employees |
208000 |
|
Annual Revenue |
€41.3 billion (2019) |
|
Founder |
Ingvar Kamprad |
|
Area Served |
Europe, Middle East, North Africa, East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Oceania, North America |
|
Headquarters |
Leiden, Netherlands |
3. IKEA PESTEL Analysis
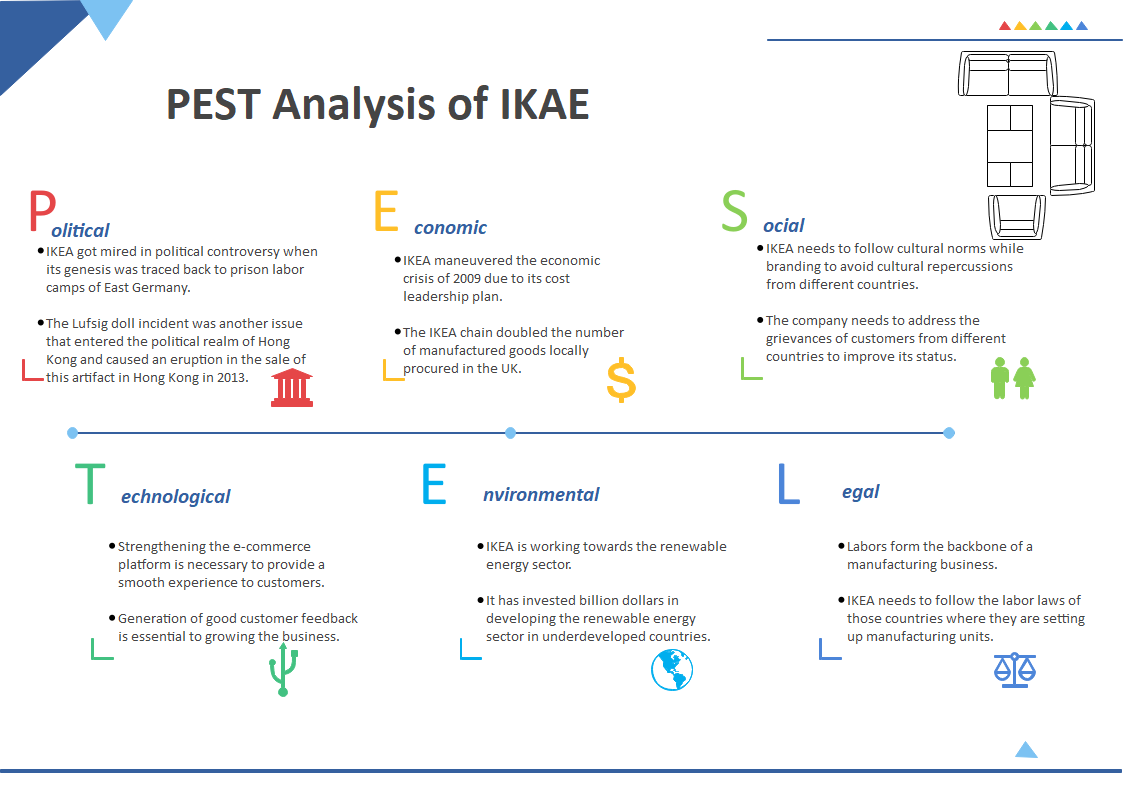
Political Factors:
Political factors are influential in understanding the expansion of a company. The political ideology of the countries where business transactions take place is an impactful factor. A stable political environment is suitable for global business organizations. The political factors affecting IKEA are:
- IKEA got mired in political controversy when its genesis was traced back to prison labor camps of East Germany. During the 1970s, IKEA suppliers used the prison labor force for manufacturing products. In 2012 a report confirmed this allegation. The company even issued a formal apology to cover up for the same. But more controversies around political issues erupted when allegations against the IKEA founder Ingvar Kamprad came to the forefront for being an active recruiter of the Swedish Nazi group. These events tarnished the image of the brand to a great extent.
- The Lufsig doll incident was another issue that entered the political realm of Hong Kong and caused an eruption in the sale of this artifact in Hong Kong in 2013. The word Lufsig was similar to a swear word in the Cantonese language. In 2013, a protestor threw the Lufsig doll at the chief executive of Honk Kong to show their dissatisfaction. The doll, however, was assumed to be a symbolic status. It was sold out in a day in Hong Kong following that incident.
- The Lobbying activities of IKEA are minimal. One can note this from the company’s expenditure in lobbying activities.
Economic Factors:
Economic conditions of a country reflect the purchasing capacity of consumers. Therefore is directly linked to the business of a company. If a company desires improved sales, it may look for regions with stable market conditions. Here are some economic issues which can impact the sales of the company:
- IKEA maneuvered the economic crisis of 2009 due to its cost leadership plan. Hence, they suffered a one percent drop in the sales volume.
- The IKEA chain doubled the number of manufactured goods locally procured in the UK. It happened due to the weakening of the pound against the euro and dollar.
- The fluctuating cost of raw materials is a vital factor that can affect the business adversely.
Social Factors:
Social conditions have affected IKEA on several accounts. PESTEL analysis IKEA reveals the impact of social conditions on the brand image of a company:
- IKEA needs to follow cultural norms while branding to avoid cultural repercussions from different countries.
- The company needs to address the grievances of customers from different countries to improve its status.
Technological Factors:
Technically IKEA, progressed by setting up an e-commerce website for the sale of products. Printed brochures for IKEA products are still in use. However, the online field is also used for expanding business. PESTEL analysis IKEA lists the challenges that it has to overcome in the technological department:
- Strengthening the e-commerce platform is necessary to provide a smooth experience to customers. Presently many customers have expressed their dissatisfaction over the poor delivery management system.
- Generation of good customer feedback is essential to growing the business. The firm should also avoid technological glitches to ensure satisfaction. They should feature the reviews and ratings through digital platforms to earn credibility.
Environmental Factors:
The world is increasingly becoming environmentally conscious. The sensitive ecological situation requires companies to adapt their production techniques to make it eco-friendly. IKEA is working to improve its technique, and the PESTEL analysis of IKEA enlists the environment-friendly steps they have taken so far:
- IKEA is working towards the renewable energy sector. It wants to use renewable energy for the stores.
- It has invested billion dollars in developing the renewable energy sector in underdeveloped countries.
- It is also working towards using sustainable materials for manufacturing products.
Legal Factors:
Legal issues have a massive impact on the growth of an organization. Pending legal cases and/or multiple lawsuits create a negative image. PESTEL analysis IKEA enlists the legal issues that should be recognized and rectified by the company:
- Labors form the backbone of a manufacturing business. IKEA has faced backlash from the workers regarding unhealthy working conditions. Works have filed lawsuits against the firm. Bad press is inevitable if laborers continue to work in poor conditions.
- IKEA needs to follow the labor laws of those countries where they are setting up manufacturing units. It ensures that laborers don’t face life-endangering situations.
- Customer satisfaction is paramount, and low-quality products can harm it. It can invite lawsuits for the company as clients can move to Court for injuries caused due to faulty products.
4. Key Takeaways
PESTEL analysis of IKEA shows that it is an established company that has maintained its zeal to grow into the global market and has performed well during an economic crisis. The challenges of IKEA are the technological and legal factors. Customer complaints are often the result of technical issues that require due consideration. The legal aspect is the most vital issue as harm to customers due to poor quality furniture can permanently tarnish the firm's image.
Use EdrawMax Online to create a PESTEL analysis diagram, or create any other diagram with ease! There are massive PESTEL templates and symbols to choose from, and creating a PESTEL analysis diagram could be really simple. Also, you can find substantial PESTEL templates in our template community to have a quick start. If you want to know more about how to make a PESTEL analysis diagram in EdrawMax Online, just check this PESTEL guide, it may help you to create diagrams without efforts.
5. References
-
Frue, K., 2021. 'PESTLE Analysis of IKEA', PESTLE Analysis, [online]. Available at: https://pestleanalysis.com/pestle-analysis-of-ikea/ (Accessed 27 June 2021).
-
Research-Methodology. 2021. 'IKEA PESTEL Analysis - Research Methodology', PESTLE Analysis, [online]. Available at: https://research-methodology.net/ikea-pest-analysis/ (Accessed 27 June 2021).
-
Shaw, A. and Shaw, A., 2021. 'PESTLE Analysis of IKEA | SWOT & PESTLE Analysis', SWOT & PESTLE Analysis ,[online]. Available at: https://swotandpestleanalysis.com/pestle-analysis-of-ikea/ (Accessed 27 June 2021).